Page 296 - Managing Global Warming
P. 296
256 Managing Global Warming
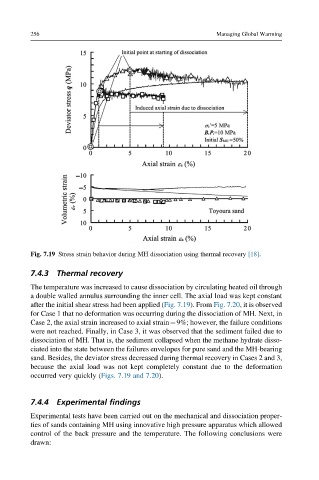
Fig. 7.19 Stress strain behavior during MH dissociation using thermal recovery [18].
7.4.3 Thermal recovery
The temperature was increased to cause dissociation by circulating heated oil through
a double walled annulus surrounding the inner cell. The axial load was kept constant
after the initial shear stress had been applied (Fig. 7.19). From Fig. 7.20, it is observed
for Case 1 that no deformation was occurring during the dissociation of MH. Next, in
Case 2, the axial strain increased to axial strain¼9%; however, the failure conditions
were not reached. Finally, in Case 3, it was observed that the sediment failed due to
dissociation of MH. That is, the sediment collapsed when the methane hydrate disso-
ciated into the state between the failures envelopes for pure sand and the MH-bearing
sand. Besides, the deviator stress decreased during thermal recovery in Cases 2 and 3,
because the axial load was not kept completely constant due to the deformation
occurred very quickly (Figs. 7.19 and 7.20).
7.4.4 Experimental findings
Experimental tests have been carried out on the mechanical and dissociation proper-
ties of sands containing MH using innovative high pressure apparatus which allowed
control of the back pressure and the temperature. The following conclusions were
drawn: