Page 298 - Managing Global Warming
P. 298
258 Managing Global Warming
1. The strength of MH sand increased with MH saturation due to particle bonding and
supporting.
2. MHBS sample will be damaged after exploitation (no matter if thermal recovery or depres-
surization process was used) when the deviator stress applied is larger than the compression
strength of pure host sand.
3. In the case of dissociation by depressurization, axial strains were generated by increasing
effective stress until a stable equilibrium was reached. However, repressurization led to
the failure in the metastable zone.
7.5 DEM simulation of MH dissociation process
Many challenges were encountered in experiments, such as difficulties in replicating
samples with the same physical properties or visualizing the changes of microscopic
structure, which is believed to underlie the macroscopic behaviors. To achieve these
objectives, numerical simulations are required.
The discrete element method (DEM) simulates granular materials (soils) as assem-
blies of individual particles. It was developed on the basis of simple interparticle con-
tact laws and has the advantage of visualizing the evolution of microscopic particle
interactions with good sample repeatability and also of low cost.
7.5.1 Reproduction of MH dissociation process using DEM
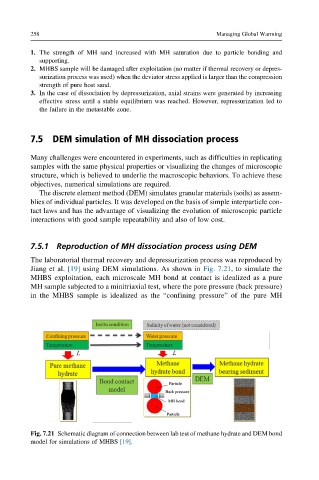
The laboratorial thermal recovery and depressurization process was reproduced by
Jiang et al. [19] using DEM simulations. As shown in Fig. 7.21,tosimulate the
MHBS exploitation, each microscale MH bond at contact is idealized as a pure
MH sample subjected to a minitriaxial test, where the pore pressure (back pressure)
in the MHBS sample is idealized as the “confining pressure” of the pure MH
Fig. 7.21 Schematic diagram of connection between lab test of methane hydrate and DEM bond
model for simulations of MHBS [19].