Page 158 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 158
Section 5.5 Carbon and Alloy Steels |37
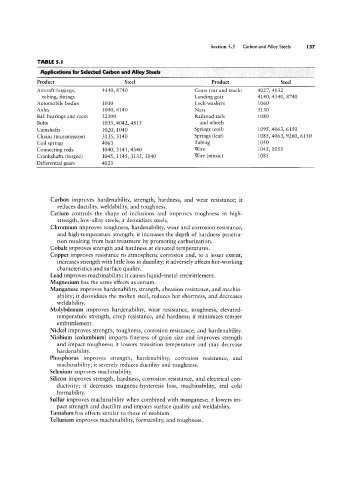
TABLE 5.I
Applications iur Selected Carbon and Alloy Steels
Product Steel Product Steel
Aircraft forgings, 4140, 8740 Gears (car and truck) 4027, 4032
tubing, fittings Landing gear 4140, 4340, 8740
Automobile bodies 1010 Lock washers 1060
Axles 1040, 4140 Nuts 3130
Ball bearings and races 52100 Railroad rails 1080
Bolts 1035, 4042, 4815 and wheels
Cgmghaftg 1020 1040 Springs (coil) 1095, 4063, 6150
Chains (transmission) 3135 3140 Springs (leaf) 1085, 4063, 9260 6150
Coil springs 4063 Tubing 1040
Connecting rods 1040, 3141, 4340 Wif€ 1045 1055
Crankshafts (forged) 1045 1145, 3135, 3140 Wife (music) 1085
Differential gears 4023
Carbon improves hardenability, strength, hardness, and wear resistance; it
reduces ductility, vveldability, and toughness.
Cerium controls the shape of inclusions and improves toughness in high-
strength, low-alloy steels; it deoxidizes steels.
Chromium improves toughness, hardenability, wear and corrosion resistance,
and high-temperature strength; it increases the depth of hardness penetra-
tion resulting from heat treatment by promoting carburization.
Cobalt improves strength and hardness at elevated temperatures.
Copper improves resistance to atmospheric corrosion and, to a lesser extent,
increases strength with little loss in ductility; it adversely affects hot-working
characteristics and surface quality.
Lead improves machinability, it causes liquid-metal embrittlement.
Magnesium has the same effects as cerium.
Manganese improves hardenability, strength, abrasion resistance, and machin-
ability; it deoxidizes the molten steel, reduces hot shortness, and decreases
weldability.
Molybdenum improves hardenability, wear resistance, toughness, elevated-
temperature strength, creep resistance, and hardness; it minimizes temper
embrittlement.
Nickel improves strength, toughness, corrosion resistance, and hardenability.
Niobium (columbium) imparts fineness of grain size and improves strength
and impact toughness; it lowers transition temperature and may decrease
hardenability.
Phosphorus improves strength, hardenability, corrosion resistance, and
machinability; it severely reduces ductility and toughness.
Selenium improves machinability,
Silicon improves strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and electrical con-
ductivity; it decreases magnetic-hysteresis loss, machinability, and cold
formability.
Sulfur improves machinability when combined with manganese; it lowers im-
pact strength and ductility and impairs surface quality and weldability.
Tantalum has effects similar to those of niobium.
Tellurium improves machinability, formability, and toughness.