Page 42 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 42
General introduction -' ¢e<§$;ea}ce,~<eeaa J
Sheet-metal-forming
. I I
LQ
Shearing Bending and drawing
Forming
'- ~-1 § , 2 ..
I""`"' """"|
" "" "'
I' °""["”"'°'
"|
§
I
I 'II,
I
I
I
:T
rrrrrr
3:16
I
,_
I ,,f,,f,,, ,,,,
Blanking | I I I . Bending Stretch forming I I I
I I
I I in I | ,:¢,3;..~~‘:'t'. I |
I I
,,,.
I
I
H
H W . VVVV IIIII I I I ml 'fi l I
Siitting I = I I Hemming = I I I Hydroforming I
‘P
I | | : I gg _
I
P ” =r~ I I
I I I I I I,,, I
l
Punching Roll forming Spinning I
I I I
I I | I
I -
I | I | i |
I I | I |
|
I I IIIIIII I I |
I I M W I_III I I I' I IIII | | | |
I I .l ‘ I ' I I ' I
I 3
'
' £ IIII
'
I
I
I I
Piercing Deep drawing I Magnetic-pulse forming I
I I I
__._____.___¢ _..____.._____¢ I _._______.__..__d
l I.
(C)
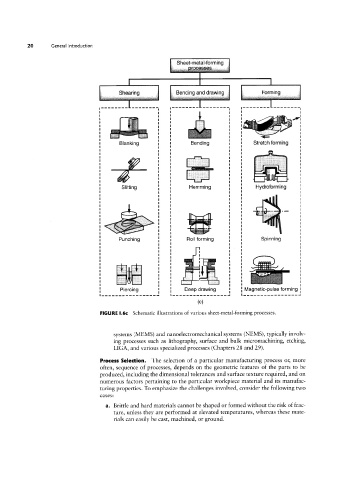
FIGURE I.6c Schematic illustrations of various sheet-metal-forming processes.
systems (MEMS) and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), typically involv-
ing processes such as lithography, surface and bulk micromachining, etching,
LIGA, and various specialized processes (Chapters 28 and 29).
Process Selection. The selection of a particular manufacturing process or, more
often, sequence of processes, depends on the geometric features of the parts to be
produced, including the dimensional tolerances and surface texture required, and on
numerous factors pertaining to the particular workpiece material and its manufac-
turing properties. To emphasize the challenges involved, consider the following two
cases:
a. Brittle and hard materials cannot be shaped or formed without the risk of frac-
ture, unless they are performed at elevated temperatures, whereas these mate-
rials can easily be cast, machined, or ground.