Page 577 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 577
Chapter 21 Fundamentals of Machining
Rough Surface Shiny surface
Rake face
Chlp Tool
Shea' Rake angle
Flank face
Relief or
clearance
angle
Shear angle
(H)
I
Rough surface
Rake face
1 Tool
Primary Hake angle
shear zone
Flank face
Rough
surface
(D)
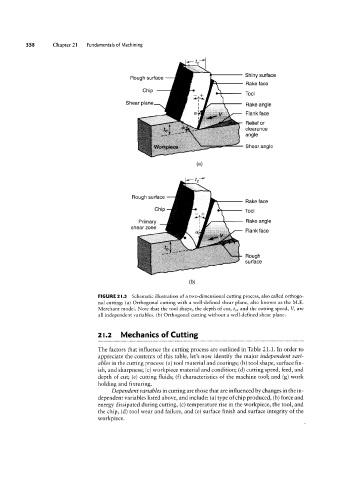
FIGURE 2I.3 Schematic illustration of a two-dimensional cutting process, also called orthogo-
nal cutting: (a) Orthogonal cutting with a well-defined shear plane, also known as the M.E.
Merchant model. Note that the tool shape, the depth of cut, to, and the cutting speed, V, are
all independent variables. (b) Orthogonal cutting without a well-defined shear plane.
2|.2 Mechanics of Cutting
The factors that influence the cutting process are outlined in Table 21.1. In order to
appreciate the contents of this table, let’s now identify the major independent vari-
ables in the cutting process: (a) tool material and coatings; (b) tool shape, surface fin-
ish, and sharpness; (C) workpiece material and condition; (d) cutting speed, feed, and
depth of cut; (e) cutting fluids; (f) characteristics of the machine tool; and (g) work
holding and fixturing.
Dependent variables in cutting are those that are influenced by changes in the in-
dependent variables listed above, and include: (a) type of chip produced, (b) force and
energy dissipated during cutting, (c) temperature rise in the workpiece, the tool, and
the chip, (d) tool wear and failure, and (e) surface finish and surface integrity of the
workpiece.