Page 120 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 120
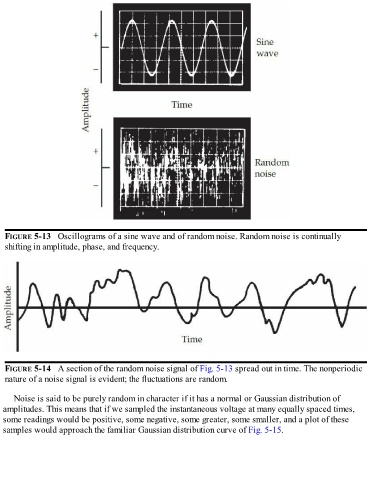
FIGURE 5-13 Oscillograms of a sine wave and of random noise. Random noise is continually
shifting in amplitude, phase, and frequency.
FIGURE 5-14 A section of the random noise signal of Fig. 5-13 spread out in time. The nonperiodic
nature of a noise signal is evident; the fluctuations are random.
Noise is said to be purely random in character if it has a normal or Gaussian distribution of
amplitudes. This means that if we sampled the instantaneous voltage at many equally spaced times,
some readings would be positive, some negative, some greater, some smaller, and a plot of these
samples would approach the familiar Gaussian distribution curve of Fig. 5-15.