Page 104 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 104
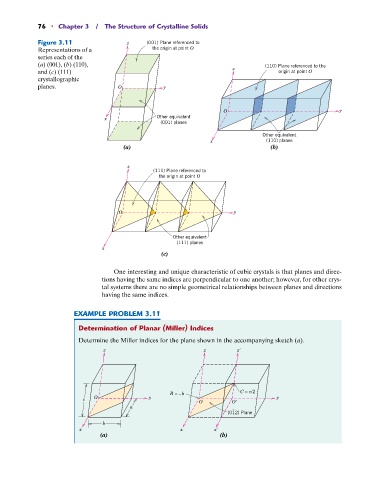
76 • Chapter 3 / The Structure of Crystalline Solids
Figure 3.11 z (001) Plane referenced to
Representations of a the origin at point O
series each of the
(a) (001), (b) (110), (110) Plane referenced to the
and (c) (111) z origin at point O
crystallographic
planes. O y
O y
Other equivalent
x
(001) planes
Other equivalent
x (110) planes
(a) (b)
z
(111) Plane referenced to
the origin at point O
O y
Other equivalent
(111) planes
x
(c)
One interesting and unique characteristic of cubic crystals is that planes and direc-
tions having the same indices are perpendicular to one another; however, for other crys-
tal systems there are no simple geometrical relationships between planes and directions
having the same indices.
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 3.11
Determination of Planar (Miller) Indices
Determine the Miller indices for the plane shown in the accompanying sketch (a).
z z z
B = –b C = c/2
O y y
c
O O
a
(012) Plane
b
x x x
(a) (b)