Page 105 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 105
3.10 Crystallographic Planes • 77
Solution
Because the plane passes through the selected origin O, a new origin must be chosen at the
corner of an adjacent unit cell. In choosing this new unit cell, we move one unit-cell distance
parallel to the y-axis, as shown in sketch (b). Thus x -y-z is the new coordinate axis system
having its origin located at O . Because this plane is parallel to the x axis its intercept is
a—that is, A a. Furthermore, from illustration (b), intersections with the y and z axes
are as follows:
B = -b C = c>2
It is now possible to use Equations 3.14a–3.14c to determine values of h, k, and l. At this point,
let us choose a value of 1 for n. Thus,
na 1a
h = = = 0
A a
nb 1b
k = = = -1
B -b
nc 1c
l = = = 2
C c>2
And finally, enclosure of the 0, 1, and 2 indices in parentheses leads to (012) as the designa-
tion for this direction. 8
This procedure is summarized as follows:
x y z
Intercepts (A, B, C) a b c/2
Calculated values of h, k, and l h 0 k 1 l 2
(Equations 3.14a–3.14c)
Enclosure (012)
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 3.12
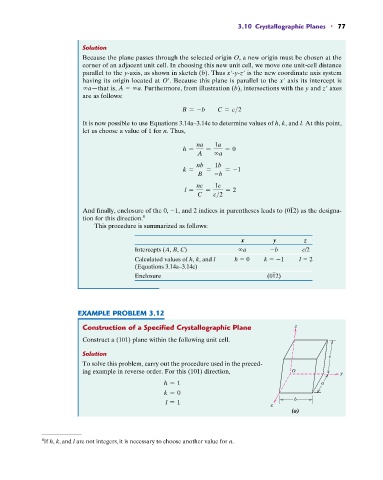
Construction of a Specified Crystallographic Plane z
Construct a (101) plane within the following unit cell.
Solution c
To solve this problem, carry out the procedure used in the preced-
ing example in reverse order. For this (101) direction, O y
h = 1 a
k = 0
b
l = 1
x
(a)
8 If h, k, and l are not integers, it is necessary to choose another value for n.