Page 56 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 56
28 • Chapter 2 / Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding
the inert, or noble, gases, which are virtually unreactive chemically. Some atoms of the
elements that have unfilled valence shells assume stable electron configurations by gain-
ing or losing electrons to form charged ions or by sharing electrons with other atoms.
This is the basis for some chemical reactions and also for atomic bonding in solids, as
explained in Section 2.6.
2
3
Concept Check 2.2 Give electron configurations for the Fe and S ions.
[The answer may be found at www.wiley.com/college/callister (Student Companion Site).]
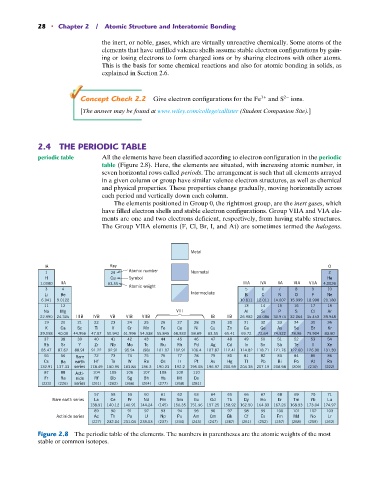
2.4 THE PERIODIC TABLE
periodic table All the elements have been classified according to electron configuration in the periodic
table (Figure 2.8). Here, the elements are situated, with increasing atomic number, in
seven horizontal rows called periods. The arrangement is such that all elements arrayed
in a given column or group have similar valence electron structures, as well as chemical
and physical properties. These properties change gradually, moving horizontally across
each period and vertically down each column.
The elements positioned in Group 0, the rightmost group, are the inert gases, which
have filled electron shells and stable electron configurations. Group VIIA and VIA ele-
ments are one and two electrons deficient, respectively, from having stable structures.
The Group VIIA elements (F, Cl, Br, I, and At) are sometimes termed the halogens.
Metal
IA Key 0
1 29 Atomic number Nonmetal 2
H Cu Symbol He
1.0080 IIA 63.55 Atomic weight IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA 4.0026
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Li Be Intermediate B C N O F Ne
6.941 9.0122 10.811 12.011 14.007 15.999 18.998 20.180
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Na Mg VIII Al Si P S Cl Ar
22.990 24.305 IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB IB IIB 26.982 28.086 30.974 32.064 35.453 39.948
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
39.098 40.08 44.956 47.87 50.942 51.996 54.938 55.845 58.933 58.69 63.55 65.41 69.72 72.64 74.922 78.96 79.904 83.80
37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
85.47 87.62 88.91 91.22 92.91 95.94 (98) 101.07 102.91 106.4 107.87 112.41 114.82 118.71 121.76 127.60 126.90 131.30
55 56 Rare 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86
Cs Ba earth Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
132.91 137.33 series 178.49 180.95 183.84 186.2 190.23 192.2 195.08 196.97 200.59 204.38 207.19 208.98 (209) (210) (222)
87 88 Acti- 104 105 106 107 108 109 110
Fr Ra nide Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds
(223) (226) series (261) (262) (266) (264) (277) (268) (281)
57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71
Rare earth series La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu
138.91 140.12 140.91 144.24 (145) 150.35 151.96 157.25 158.92 162.50 164.93 167.26 168.93 173.04 174.97
89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103
Actinide series Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr
(227) 232.04 231.04 238.03 (237) (244) (243) (247) (247) (251) (252) (257) (258) (259) (262)
Figure 2.8 The periodic table of the elements. The numbers in parentheses are the atomic weights of the most
stable or common isotopes.