Page 221 - Mathematical Models and Algorithms for Power System Optimization
P. 221
212 Chapter 6
Start
Seek initial exploration points
with expert rules, Set the GA
parameters
Current exploration points
power flow or MIP method
Yes
Whether feasible? Improve the results
No
GA operation under
expert rules
Form new exploration points
No
Judge whether satisfying
stop criterion
Yes
Stop
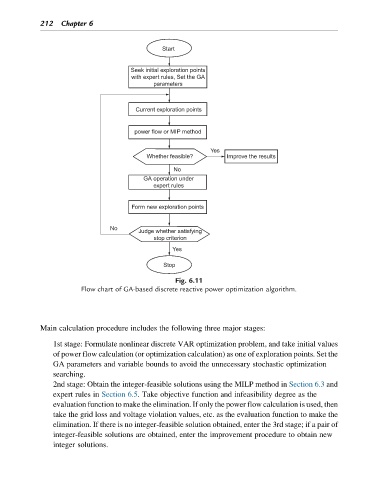
Fig. 6.11
Flow chart of GA-based discrete reactive power optimization algorithm.
Main calculation procedure includes the following three major stages:
1st stage: Formulate nonlinear discrete VAR optimization problem, and take initial values
of power flow calculation (or optimization calculation) as one of exploration points. Set the
GA parameters and variable bounds to avoid the unnecessary stochastic optimization
searching.
2nd stage: Obtain the integer-feasible solutions using the MILP method in Section 6.3 and
expert rules in Section 6.5. Take objective function and infeasibility degree as the
evaluation function to make the elimination. If only the power flow calculation is used, then
take the grid loss and voltage violation values, etc. as the evaluation function to make the
elimination. If there is no integer-feasible solution obtained, enter the 3rd stage; if a pair of
integer-feasible solutions are obtained, enter the improvement procedure to obtain new
integer solutions.