Page 222 - Mathematical Models and Algorithms for Power System Optimization
P. 222
Discrete Optimization for Reactive Power Planning 213
3rd stage: Generate new exploration points with GA, that is, reset the solution and variable
bounds to the problem. When the exploration points have been over M (generally 10–50,
given based on the calculation scale and experience), it is believed that the problem has no
integer-feasible solution stop exploring; otherwise re-enter the 2nd stage.
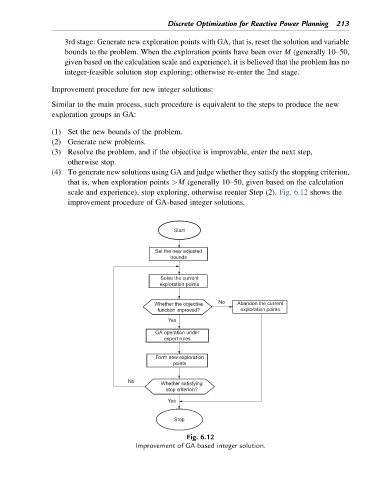
Improvement procedure for new integer solutions:
Similar to the main process, such procedure is equivalent to the steps to produce the new
exploration groups in GA:
(1) Set the new bounds of the problem.
(2) Generate new problems.
(3) Resolve the problem, and if the objective is improvable, enter the next step,
otherwise stop.
(4) To generate new solutions using GA and judge whether they satisfy the stopping criterion,
that is, when exploration points >M (generally 10–50, given based on the calculation
scale and experience), stop exploring, otherwise reenter Step (2). Fig. 6.12 shows the
improvement procedure of GA-based integer solutions.
Start
Set the new adjusted
bounds
Solve the current
exploration points
Whether the objective No Abandon the current
function improved? exploration points
Yes
GA operation under
expert rules
Form new exploration
points
No
Whether satisfying
stop criterion?
Yes
Stop
Fig. 6.12
Improvement of GA-based integer solution.