Page 289 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 289
ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS 277
If R, is the resistance at 0 "C, then the resistance R, at where: Q = temperature coefficient of resistance.
T"C is:
The value of Q is given for a number of metals as well as
R, = R,(1 + QT) electrolytes and semi-conductors in the table below.
Resistance temperature coefficients (at room temperature) "C-
~
Material a ("c-') Material Q ("c-')
~~ ~~
Nickel 0.0067 Gold 0.004
Iron 0.002-0.006 Platinum 0.00392
Tungsten 0.0048 Mercury 0.00099
Aluminium 0.0045 Manganin f0.00002
Copper 0.0043 Carbon -0.0007
Lead 0.0042 Electrolytes -0.02 to -0.09
Silver 0.0041 Semi-conduct or
(thermistor) -0.068 to +0.14
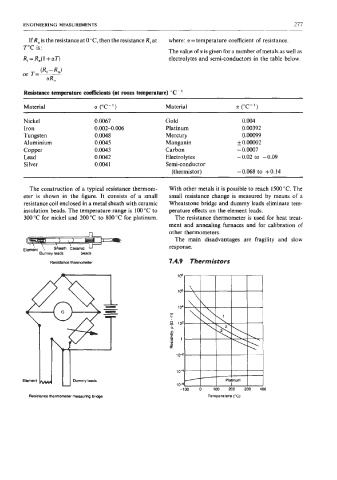
The construction of a typical resistance thermom- With other metals it is possible to reach 1500 "C. The
eter is shown in the figure. It consists of a small small resistance change is measured by means of a
resistance coil enclosed in a metal sheath with ceramic Wheatstone bridge and dummy leads eliminate tem-
insulation beads. The temperature range is 100 "C to perature effects on the element leads.
300 "C for nickel and 200 "C to 800 "C for platinum. The resistance thermometer is used for heat treat-
ment and annealing furnaces and for calibration of
other thermometers.
The main disadvantages are fragility and slow
response.
Dummy leads beads
7.4.9 Thermistors
Resistance thermometer measuring brii Temperature ("C)