Page 291 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 291
ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS 279
7.5 Pressure measurement
7.5. I Pressure units Aneroid barometer
1 newton per square metre (1 N m- 2, = 1 pascal (1 Pa) A sealed flexible metal bellows or capsule with a very
1 bar= 1OOOOO (1OS)Pa= lo00 millibar (mbar) low internal pressure is connected to a lever with
1 mbar = 100 Pa pointer and scale. Atmospheric-pressure variations
1 bar = 760 mm Hg (approximately) cause a corresponding deflection of the capsule and
movement of the pointer. The pointer usually carries a
7.5.2 Barometers pen which records the temperature on a rotating chart.
Mercury barometers
Mercury barometer
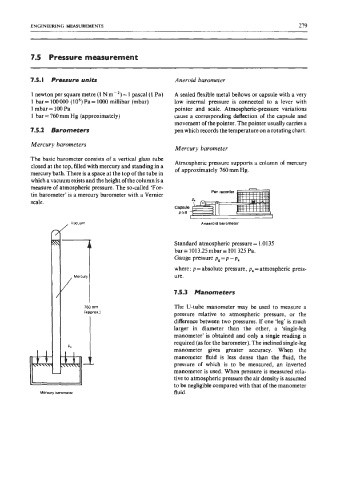
The basic barometer consists of a vertical glass tube
closed at the top, filled with mercury and standing in a Atmospheric pressure supports a column of mercury
mercury bath. There is a space at the top of the tube in of approximately 760 mm Hg.
which a vacuum exists and the height of the column is a
measure of atmospheric pressure. The so-called ‘For-
tin barometer’ is a mercury barometer with a Vernier
scale.
Anaeroid barometer
/ Vacuum
Standard atmospheric pressure= 1.0135
bar = 1013.25 mbar 101 325 Pa.
Gauge pressure p, = p -pa
where: p = absolute pressure, pa = atmospheric press-
ure.
/ Mercury
7.5.3 Manometers
The U-tube manometer may be used to measure a
pressure relative to atmospheric pressure, or the
difference between two pressures. If one ‘leg’ is much
larger in diameter than the other, a ‘single-leg
manometer’ is obtained and only a single reading is
required (as for the barometer). The inclined single-leg
manometer gives greater accuracy. When the
manometer fluid is less dense than the fluid, the
pressure of which is to be measured, an inverted
manometer is used. When pressure is measured rela-
tive to atmospheric pressure the air density is assumed
to be negligible compared with that of the manometer
Mercury barometer fluid.