Page 296 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 296
284 MECHANiCAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
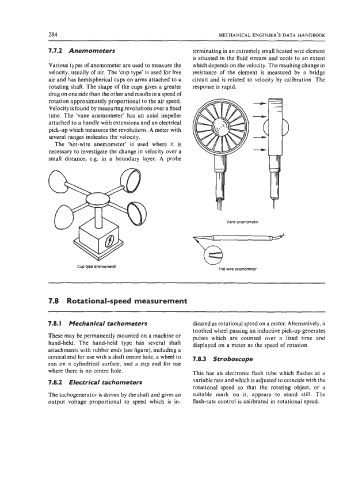
7.7.2 Anemometers terminating in an extremely small heated wire element
is situated in the fluid stream and cools to an extent
Various types of anemometer are used to measure the which depends on the velocity. The resulting change in
velocity, usually of air. The ‘cup type’ is used for free resistance of the element is measured by a bridge
air and has hemispherical cups on arms attached to a circuit and is related to velocity by calibration. The
rotating shaft. The shape of the cups gives a greater response is rapid.
drag on one side than the other and results in a speed of
rotation approximately proportional to the air speed.
Velocity is found by measuring revolutions over a fixed
time. The ‘vane anemometer’ has an axial impeller
attached to a handle with extensions and an electrical
pick-up which measures the revolutions. A meter with
several ranges indicates the velocity.
The ‘hot-wire anemometer’ is used where it is
necessary to investigate the change in velocity over a
small distance, e.g. in a boundary layer. A probe
r
Vane anemometer
Cuptype anemometer Hot-wire anemometer
7.8 Rotational-speed measurement
7.0. I Mechanical tachometers dicated as rotational speed on a meter. Alternatively, a
toothed wheel passing an inductive pick-up generates
These may be permanently mounted on a machine or pulses which are counted over a fixed time and
hand-held. The hand-held type has several shaft displayed on a meter as the speed of rotation.
attachments with rubber ends (see figure), including a
conical end for use with a shaft centre hole, a wheel to 7.0.3 Stroboscope
run on a cylindrical surface, and a cup end for use
where there is no centre hole. This has an electronic flash tube which flashes at a
7.0.2 Electrical tachometers variable rate and which is adjusted to coincide with the
rotational speed so that the rotating object, or a
The tachogenerator is driven by the shaft and gives an suitable mark on it, appears to stand still. The
output voltage proportional to speed which is in- flash-rate control is calibrated in rotational speed.