Page 293 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 293
ENGINEERING MEASUREMENTS 28 1
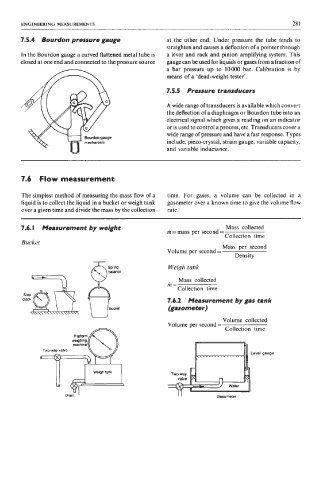
7.5.4 Bourdon pressure gauge at the other end. Under pressure the tube tends to
straighten and causes a deflection of a pointer through
In the Bourdon gauge a curved flattened metal tube is a lever and rack and pinion amplifying system. This
closed at one end and connected to the pressure source gauge can be used for liquids or gases from a fraction of
a bar pressure up to loo00 bar. Calibration is by
means of a ‘dead-weight tester’.
7.5.5 Pressure transducers
A wide range of transducers is available which convert
the deflection of a diaphragm or Bourdon tube into an
electrical signal which gives a reading on an indicator
or is used to control a process, etc. Transducers cover a
wide range of pressure and have a fast response. Types
include, piezo-crystal, strain gauge, variable capacity,
and variable inductance.
7.6 Flow measurement
The simplest method of measuring the mass flow of a time. For gases, a volume can be collected in a
liquid is to collect the liquid in a bucket or weigh tank gasometer over a known time to give the volume flow
over a given time and divide the mass by the collection rate.
7.6. I Measurement by weight Mass collected
riI = mass per second =
Collection time
Bucket
Mass per second
Volume per second =
Density
Weigh tank
Mass collected
m=
Collection time
7.6.2 Measurement by gas tank
(gasometer)
Volume collected
Volume per second =
Collection time
Two-way valve
Level
Weigh tank
Gasometer