Page 338 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 338
5 Approaches to Linear Systems Analysis 329
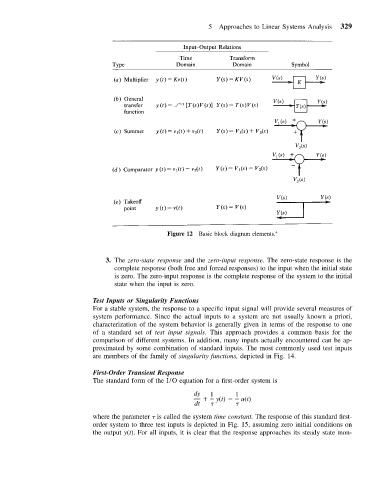
Figure 12 Basic block diagram elements. 4
3. The zero-state response and the zero-input response. The zero-state response is the
complete response (both free and forced responses) to the input when the initial state
is zero. The zero-input response is the complete response of the system to the initial
state when the input is zero.
Test Inputs or Singularity Functions
For a stable system, the response to a specific input signal will provide several measures of
system performance. Since the actual inputs to a system are not usually known a priori,
characterization of the system behavior is generally given in terms of the response to one
of a standard set of test input signals. This approach provides a common basis for the
comparison of different systems. In addition, many inputs actually encountered can be ap-
proximated by some combination of standard inputs. The most commonly used test inputs
are members of the family of singularity functions, depicted in Fig. 14.
First-Order Transient Response
The standard form of the I/O equation for a first-order system is
dy 1 1
y(t) u(t)
dt
where the parameter is called the system time constant. The response of this standard first-
order system to three test inputs is depicted in Fig. 15, assuming zero initial conditions on
the output y(t). For all inputs, it is clear that the response approaches its steady state mon-