Page 374 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 374
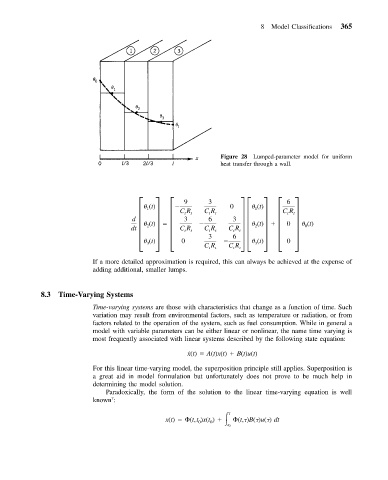
8 Model Classifications 365
Figure 28 Lumped-parameter model for uniform
heat transfer through a wall.
3
CR t CR t 0 6
3
9
6
(t)
(t)
1
1
CR
t
t
t
t
d (t) 3 6 3 (t) 0 (t)
dt 2 C R t C R t C R t 2 0
t
t
t
(t) 0 (t) 0
3
3
CR t CR t
t
t
If a more detailed approximation is required, this can always be achieved at the expense of
adding additional, smaller lumps.
8.3 Time-Varying Systems
Time-varying systems are those with characteristics that change as a function of time. Such
variation may result from environmental factors, such as temperature or radiation, or from
factors related to the operation of the system, such as fuel consumption. While in general a
model with variable parameters can be either linear or nonlinear, the name time varying is
most frequently associated with linear systems described by the following state equation:
˙ x(t) A(t)x(t) B(t)u(t)
For this linear time-varying model, the superposition principle still applies. Superposition is
a great aid in model formulation but unfortunately does not prove to be much help in
determining the model solution.
Paradoxically, the form of the solution to the linear time-varying equation is well
known :
7
t
x(t) (t,t )x(t ) (t, )B( )u( ) dt
0
0
t 0