Page 360 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 360
4 Heat-Pipe Fabrication Processes 349
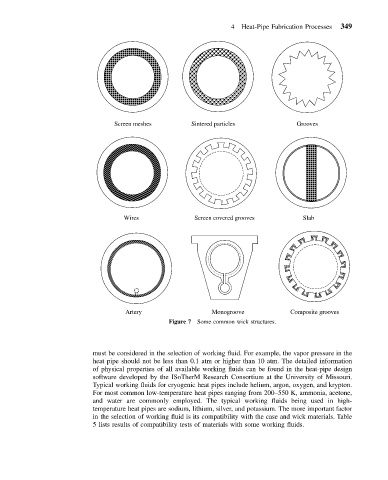
Screen meshes Sintered particles Grooves
Wires Screen covered grooves Slab
Artery Monogroove Composite grooves
Figure 7 Some common wick structures.
must be considered in the selection of working fluid. For example, the vapor pressure in the
heat pipe should not be less than 0.1 atm or higher than 10 atm. The detailed information
of physical properties of all available working fluids can be found in the heat-pipe design
software developed by the ISoTherM Research Consortium at the University of Missouri.
Typical working fluids for cryogenic heat pipes include helium, argon, oxygen, and krypton.
For most common low-temperature heat pipes ranging from 200–550 K, ammonia, acetone,
and water are commonly employed. The typical working fluids being used in high-
temperature heat pipes are sodium, lithium, silver, and potassium. The more important factor
in the selection of working fluid is its compatibility with the case and wick materials. Table
5 lists results of compatibility tests of materials with some working fluids.