Page 93 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 93
82 Fluid Mechanics
p p ƒL k
1
2
V /2 D h L
where p is the pressure at the duct inlet and p is the pressure a distance L from the inlet.
1
The value of k depends on L but becomes a constant in the fully developed region, and this
L
constant value is of greatest interest.
For laminar flow the pressure drop in the entrance length L is obtained from the
e
Bernoulli equation written along the duct axis where there is no shear in the core flow.
This is
u
u 2 max V 2 2 1 V 2
max
p p
e
1
2 2 V 2
for any duct for which u max /V is known. When both friction factor and k are known, the
L
entrance length is
2 1 k
L e 1 u max
D h ƒ V L
For a circular duct, experiments and analyses indicate that k
1.30. Thus, for a circular
L
duct, L /D (Re /64)(2 1 1.30) 0.027Re . The pressure drop for fully developed
2
D
e
D
flow in a length L is
p 1.70 V /2 and thus the pressure drop in the entrance is 3/1.70
2
e
1.76 times that in an equal length for fully developed flow. Entrance effects are important
for short ducts.
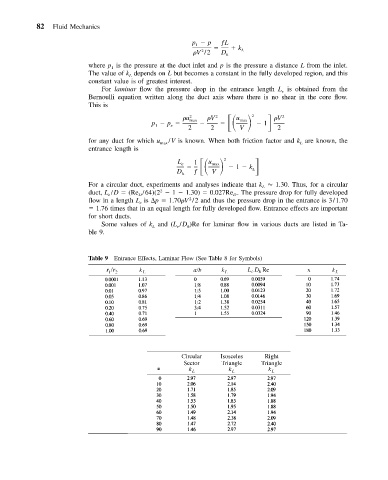
Some values of k and (L /D )Re for laminar flow in various ducts are listed in Ta-
e
L
h
ble 9.
Table 9 Entrance Effects, Laminar Flow (See Table 8 for Symbols)