Page 118 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 118
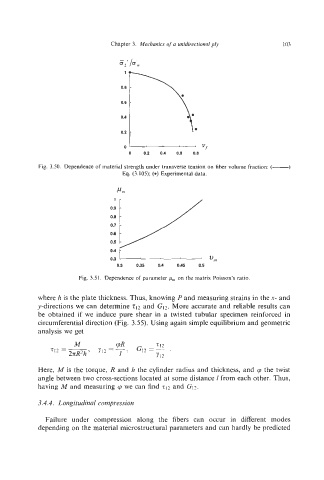
Chapter 3. Mechanics of a unidirectional ply 103
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0 “f
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Fig. 3.50. Dependence of material strength under transverse tension on fiber volume fraction: (-)
EQ. (3.105); (a) Experimental data.
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.3 L
v,,
0.4
0.3 035 0.4 0.45 0.5
Fig. 3.5 I. Dependence of parameter p,,, on the matrix Poisson’s ratio.
where 11 is the plate thickness. Thus, knowing P and measuring strains in the x- and
y-directions we can determine T12 and G12. More accurate and reliable results can
be obtained if we induce pure shear in a twisted tubular specimen reinforced in
circumferential direction (Fig. 3.55). Using again simple equilibrium and geometric
analysis we get
M (PR
212
?I2 = - GI?=- .
~12=-,
2nR2h ’ I Y12
Here, M is the torque, R and h the cylinder radius and thickness, and cp the twist
angle between two cross-sections located at some distance I from each other. Thus,
having M and measuring cp we can find f12 and GI?.
3.4.4. Longitudinal compression
Failure under compression along the fibers can occur in different modes
depending on the material microstructural parameters and can hardly be predicted