Page 181 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 181
166 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
Substituting Eqs. (4.105) into Eqs. (4.104) and using Eqs. (4.103) we arrive at
where
4.4.2. Nonlinear models
Nonlinear behavior of a cross-ply layer associated with nonlinear material
response under loading in the principal material coordinates (see, e.g., Figs. 4.16
and 4.17) can be described using nonlinear constitutive equations, Eqs. (4.60) or
Eqs. (4.64) instead of linear equations (4.99).
However, this layer can demonstrate nonlinearity that is entirely different from
what was studied in the previous sections. This nonlinearity is observed in the cross-
ply layer composed of linear elastic plies and is caused by microcracking of the
matrix.
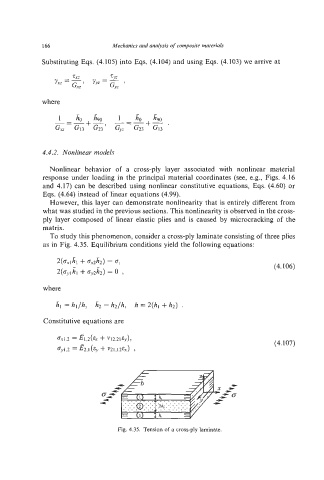
To study this phenomenon, consider a cross-ply laminate consisting of three plies
as in Fig. 4.35. Equilibrium conditions yield the following equations:
2(6,lhl + cx2h2) = 6, (4.106)
2(q,lh, + qv2h2) = 0 ,
where
A, = hl/h, h2 = hz/h, h = 2(hl + h2) .
Constitutive equations are
011.2 = El,2(Ex + V12.21&y), (4.107)
cy1.2 = E2,, (E.” + V21.12Ex) ,
Fig. 4.35. Tension of a cross-ply laminate.