Page 331 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 331
316 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
T, "c
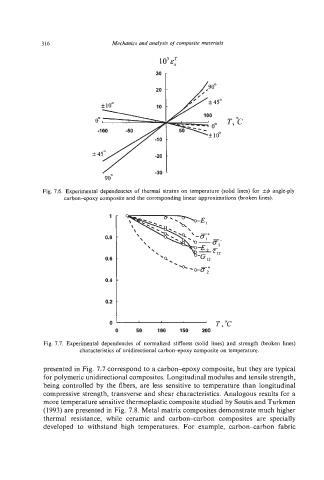
Fig. 7.6. Experimental dependencies of thermal strains on temperature (solid lines) for +4 angle-ply
carbon-epoxy composite and the correspondinglinear approximations(broken lines).
1-
0.8 -
0.6 -
Om4 t
L
O 0 0 50 100 2 150 200 T,oC
m
Fig. 7.7. Experimental dependencies of normalized stiffness (solid lines) and strength (broken lines)
characteristics of unidirectionalcarbon-epoxy composite on temperature.
presented in Fig. 7.7 correspond to a carbon+poxy composite, but they are typical
for polymeric unidirectional composites. Longitudinal modulus and tensile strength,
being controlled by the fibers, are less sensitive to temperature than longitudinal
compressive strength, transverse and shear characteristics. Analogous results for a
more temperature sensitive thermoplastic composite studied by Soutis and Turkmen
(1993) are presented in Fig. 7.8. Metal matrix composites demonstrate much higher
thermal resistance, while ceramic and carbon-carbon composites are specially
developed to withstand high temperatures. For example, carbon-carbon fabric