Page 334 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 334
Chapter 7. Environmental, special loading, and manufacturing effects 3 19
effect of aging, test under transverse bending (see Fig. 4.95) is usually performed.
Thus found flexural strength
3Pl
ijf = -
2bh'
allows for both fiber and matrix material degradation in the process of aging.
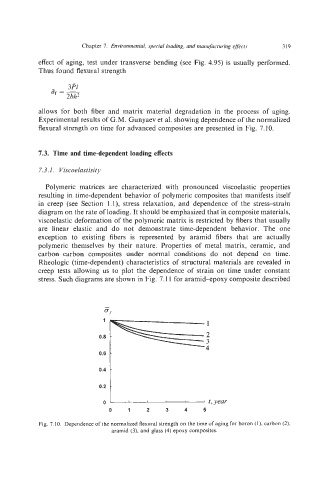
Experimental results of G.M. Gunyaev et al. showing dependence of the normalized
flexural strength on time for advanced composites are presented in Fig. 7.10.
7.3. Time and timedependent loading effects
7.3.I. Viscoelastisity
Polymeric matrices are characterized with pronounced viscoelastic properties
resulting in time-dependent behavior of polymeric composites that manifests itself
in creep (see Section ].I), stress relaxation, and dependence of the stress-strain
diagram on the rate of loading. It should be emphasized that in composite materials,
viscoelastic deformation of the polymeric matrix is restricted by fibers that usually
are linear elastic and do not demonstrate time-dependent behavior. The one
exception to existing fibers is represented by aramid fibers that are actually
polymeric themselves by their nature. Properties of metal matrix, ceramic, and
carbon-carbon composites under normal conditions do not depend on time.
Rheologic (time-dependent) characteristics of structural materials are revealed in
creep tests allowing us to plot the dependence of strain on time under constant
stress. Such diagrams are shown in Fig. 7. I 1 for aramid-poxy composite described
1
2
3
4
0.6
-
0.4
-
0.2
o t,year
0 1 2 3 4 5
Fig. 7.10. Dependence of the normalized flexural strength on the time of aging for boron (I),carbon (2).
aramid (3). and glass (4)epoxy composites.