Page 339 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 339
324 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
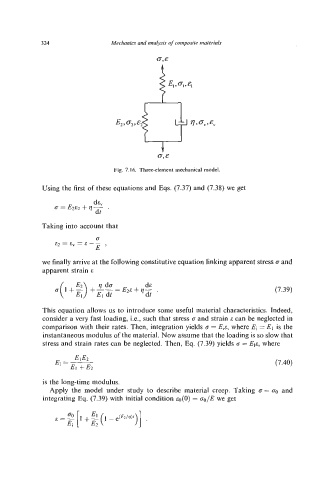
Fig. 7.16. Three-element mechanical model.
Using the first of these equations and Eqs. (7.37) and (7.38) we get
de,
a =Em +q-
dt
Taking into account that
E2 = Ev = E - -
E'
we finally arrive at the following constitutive equation linking apparent stress a and
apparent strain E
(7.39)
This equation allows us to introduce some useful material characteristics. Indeed,
consider a very fast loading, i.e., such that stress a and strain E can be neglected in
comparison with their rates. Then, integration yields a =E,&, where Ei =E1 is the
instantaneous modulus of the material. Now assume that the loading is so slow that
stress and strain rates can be neglected. Then, Eq. (7.39) yields Q = El&,where
(7.40)
is the long-time modulus.
Apply the model under study to describe material creep. Taking a = go and
integrating Eq. (7.39) with initial condition eo(0) = ao/E we get