Page 347 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 347
332 Mechanics and analysis of composite materials
P = 6MPa
0.8 ' 7
[ , , , , t,Days(24Hours)
0
0 5 10 15 20
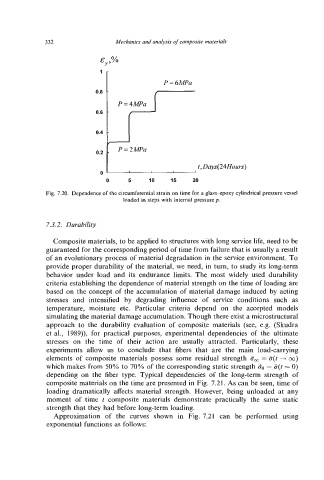
Fig. 7.20. Dependence of the circumferential strain on time for a glass-epoxy cylindrical pressure vessel
loaded in steps with internal pressure p.
7.3.2. Durability
Composite materials, to be applied to structures with long service life, need to be
guaranteed for the corresponding period of time from failure that is usually a result
of an evolutionary process of material degradation in the service environment. To
provide proper durability of the material, we need, in turn, to study its long-term
behavior under load and its endurance limits. The most widely used durability
criteria establishing the dependence of material strength on the time of loading are
based on the concept of the accumulation of material damage induced by acting
stresses and intensified by degrading influence of service conditions such as
temperature, moisture etc. Particular criteria depend on the accepted models
simulating the material damage accumulation. Though there exist a microstructural
approach to the durability evaluation of composite materials (see, e.g. (Skudra
et al., 1989)), for practical purposes, experimental dependencies of the ultimate
stresses on the time of their action are usually attracted. Particularly, these
experiments allow us to conclude that fibers that are the main load-carrying
elements of composite materials possess some residual strength am= a(t -, 00)
which makes from 50% to 70% of the corresponding static strength CO= a(t = 0)
depending on the fiber type. Typical dependencies of the long-term strength of
composite materials on the time are presented in Fig. 7.21. As can be seen, time of
loading dramatically affects material strength. However, being unloaded at any
moment of time t composite materials demonstrate practically the same static
strength that they had before long-term loading.
Approximation of the curves shown in Fig. 7.21 can be performed using
exponential functions as follows: