Page 348 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 348
Chapter I. Environmental. special loading, and manufacturing effects 333
0
0 100 200 300 400 500
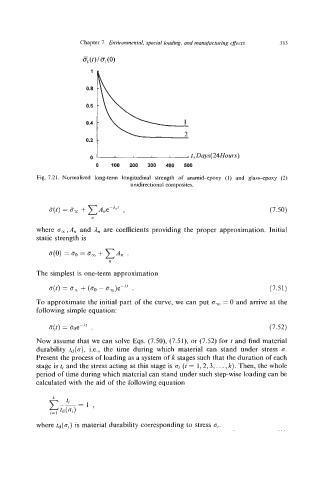
Fig. 7.21. Normalized long-term longitudinal strength of aramid-epoxy (1) and glass-epoxy (2)
unidirectional composites.
(7.50)
n
where e,, A,, and A,, are coefficients providing the proper approximation. Initial
static strength is
a(0) = i30 = ax + EA,,.
n
The simplest is one-term approximation
~(t)= 0, + (00 - @,)e-”‘ . (7.51)
To approximate the initial part of the curve, we can put 0, = 0 and arrive at the
following simple equation:
~(t)= ooe-”‘ . (7.52)
Now assume that we can solve Eqs. (7.50), (7.51), or (7.52) for t and find material
durability td(e), i.e., the time during which material can stand under stress e.
Present the process of loading as a system of k stages such that the duration of each
stage is ti and the stress acting at this stage is ci (i = 1,2,3,...,k). Then, the whole
period of time during which material can stand under such step-wise loading can be
calculated with the aid of the following equation
k
X&=l,
I
i=
where td(ci) is material durability corresponding to stress ci.