Page 96 - Mechanics of Asphalt Microstructure and Micromechanics
P. 96
Microstructure Characterization 89
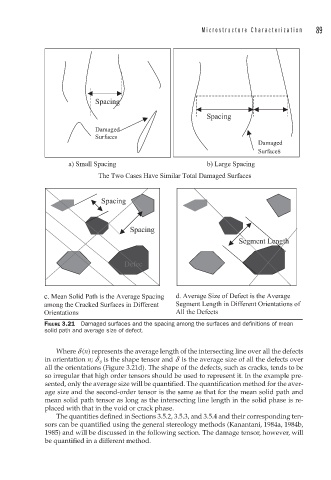
FIGURE 3.21 Damaged surfaces and the spacing among the surfaces and defi nitions of mean
solid path and average size of defect.
Where d (n) represents the average length of the intersecting line over all the defects
in orientation n; d ij is the shape tensor and d is the average size of all the defects over
all the orientations (Figure 3.21d). The shape of the defects, such as cracks, tends to be
so irregular that high order tensors should be used to represent it. In the example pre-
sented, only the average size will be quantified. The quantification method for the aver-
age size and the second-order tensor is the same as that for the mean solid path and
mean solid path tensor as long as the intersecting line length in the solid phase is re-
placed with that in the void or crack phase.
The quantities defined in Sections 3.5.2, 3.5.3, and 3.5.4 and their corresponding ten-
sors can be quantified using the general stereology methods (Kanantani, 1984a, 1984b,
1985) and will be discussed in the following section. The damage tensor, however, will
be quantified in a different method.