Page 110 - Mechatronics for Safety, Security and Dependability in a New Era
P. 110
Ch20-I044963.fm Page 94 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 5:47 PM
Ch20-I044963.fm
94 94 Page 94 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 5:47 PM
operations such as inputting the map of the environment should be avoided. And to hold down the cost,
quantity of sensors installed should be minimized. Coping the trouble within the case of human
moving the robot to the place somewhere else, also known as kidnapped robot problem [2] will also
be needed. Tn these perspectives, it is likely to adopt reactive method rather than planning-based.
While commercial robot cleaners for domestic have various devices to sweeping algorithms, there is
still room for improvement in the reactive motion algorithm. Frequency of sweeping, for example,
tends to left uneven.
The main target of this research is to promote the efficiency of reactive motion algorithm installed in
robot cleaner by establishing the way to evaluate the motion algorithm.
II. INITIAL CONDITION SET UP
This paper discusses mainly about the aspect of sweeping motion. Aspects dependent on hardware such
as vacuum performance or speed of sweeping robot are not the subjects to argue here.
To clarify the problems, we assume the conditions of sweeping task written below.
• Sweeping certain place would be done in a passage.
• The robot can cover the whole sweeping area.
• To compare the algorithms, specifications of the robot are unified.
Assuming that sweeping task of a place should complete in one passage, high performance would be
gained by minimizing overlap, and spreading the areas swept in early step. Therefore, the algorithm
can be evaluated by inspecting the sweeping rate, completed swept area divided by the area of
sweep-able.
To evaluate the sweeping rate, factors that give influence should be controlled. The considerable
factors of the sweeping robots are shape of the room and robot, and motion of the robot.
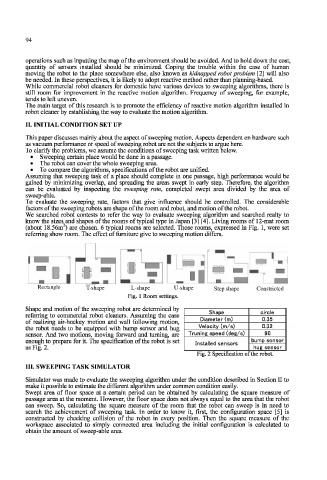
We searched robot contests to refer the way to evaluate sweeping algorithm and searched realty to
know the sizes and shapes of the rooms of typical type in Japan [3] [4]. Living rooms of 12-mat room
2
(about 18.56m ) are chosen. 6 typical rooms are selected. Those rooms, expressed in Fig. 1, were set
referring show room. The effect of furniture give to sweeping motion differs.
Rectangle T-shape L-shape U-shape Step shape Constricted
U-shape
L-shape
Rectangle
T-shape
shape
Step
Constricted
Fig. 1 Room settings.
Shape and motion of the sweeping robot are determined by Shape circle
referring to commercial robot cleaners. Assuming the case
of realizing air-hockey motion and wall following motion, Diameter (m) 0.35
the robot needs to be equipped with bump sensor and hug Velocity (m/s) 0.32
sensor. And two motions, moving forward and turning, are Truning speed (deg/s) 90
enough to prepare for it. The specification of the robot is set Installed sensors bump sensor
as Fig. 2. hug sensor
Fig. 2 Specification of the robot.
ITT. SWEEPING TASK SIMULATOR
Simulator was made to evaluate the sweeping algorithm under the condition described in Section 11 to
make it possible to estimate the different algorithm under common condition easily.
Swept area of floor space at a certain period can be obtained by calculating the square measure of
passage area at the moment. However, the floor space does not always equal to the area that the robot
can sweep. So, calculating the square measure of the room that the robot can sweep is in need to
search the achievement of sweeping task. In order to know it, first, the configuration space [5] is
constructed by checking collision of the robot in every position. Then the square measure of the
workspace associated to simply connected area including the initial configuration is calculated to
obtain the amount of sweep-able area.