Page 101 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 101
Industrial waters 81
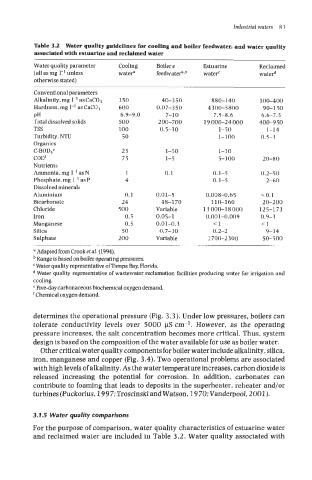
Table 3.2 Water quality guidelines for cooling and boiler feedwater, and water quality
associated with estuarine and reclaimed water
Water quality parameter Cooling Boiler e Estuarine Reclaimed
(all as mg 1-' unless watera feedwatera.b watef waterd
otherwise stated)
Conventional parameters
Alkalinity, mg 1-l as CaC03 350 40-350 880-140 100-400
Hardness, mg I-' as CaC03 600 0.07-350 4300-5800 90-150
PH 6.9-9.0 7-10 7.5-8.6 6.6-7.5
Total dissolved solids 500 200-700 19 000-24 000 400-950
TSS 100 0.5-10 1-50 1-14
Turbidity, NTU 50 1-100 0.5-3
Organics
C-BOD je 25 1-50 1-30
CODf 75 1-5 5-100 20-80
Nutrients
Ammonia, mg IF1 as N 1 0.1 0.1-5 0.2-50
Phosphate, mg 1-l as P 4 0.1-5 2-60
Dissolved minerals
A 1 urn i n i u m 0.1 0.01-5 0.008-0.65 <O.l
Bicarbonate 24 48-1 70 110-160 20-200
Chloride 500 Variable 13 000-18 000 125-173
Iron 0.5 0.05-1 0.001-0.009 0.9-3
Manganese 0.5 0.01-0.3 <1 <1
Silica 50 0.7-30 0.2-2 9-34
Sulphate 200 Variable 1700-2300 50-500
a Adapted from Crook et a!. (1994).
Range is based on boiler operating pressures.
Water quality representative of Tampa Bay, Florida.
Water quality representative of wastewater reclamation facilities producing water for irrigation and
cooling.
e Five-day carbonaceous biochemical oxygen demand.
Chemical oxygen demand.
determines the operational pressure (Fig. 3.3). Under low pressures, boilers can
tolerate conductivity levels over 5000 pS cm-l. However, as the operating
pressure increases, the salt concentration becomes more critical. Thus, system
design is based on the composition of the water available for use as boiler water.
Other critical water quality components for boiler water include alkalinity, silica,
iron, manganese and copper (Fig. 3.4). Two operational problems are associated
with high levels of alkalinity. As the water temperature increases, carbon dioxide is
released increasing the potential for corrosion. In addition, carbonates can
contribute to foaming that leads to deposits in the superheater, reheater and/or
turbines (Puckorius, 199 7; Troscinski and Watson, 19 70; Vanderpool, 2001).
3.1.5 Water quality comparisons
For the purpose of comparison, water quality characteristics of estuarine water
and reclaimed water are included in Table 3.2. Water quality associated with