Page 74 - Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use
P. 74
54 Membranes for lndustrial Wastewater Recovery und Re-ube
circumstances, it is advantageous to combine streams from modules operating in
parallel in order to maximise utilisation of the membrane elements, such that an
array of modules is produced (Fig. 2.20). This is known as staging, and is very
common in the RO treatment of thin to light brackish waters where the retentate
solution osmotic pressure does not become excessive through its concentration
along the length of the module.
It is not necessarily feasible or desirable for the retentate to be staged in order
to maximise the overall recovery. For high-salinity feedwaters, typically
seawater where osmotic pressures in the region of tens of bar prevail, further
concentration of these waters would demand uneconomically large operating
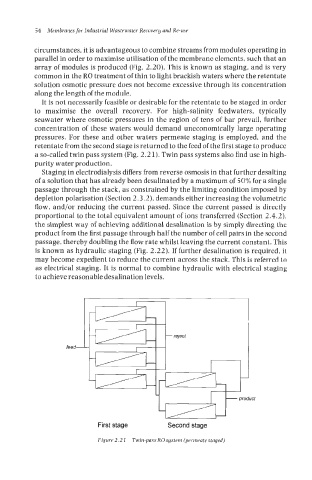
pressures. For these and other waters permeate staging is employed, and the
retentate from the second stage is returned to thc feed of the first stage to produce
a so-called twin pass system (Fig. 2.21). Twin pass systems also find use in high-
purity water production.
Staging in electrodialysis differs from reverse osmosis in that further desalting
of a solution that has already been desalinated by a maximum of 50% for a single
passage through the stack, as constrained by the limiting condition imposed by
depletion polarisation (Section 2.3.2), demands either increasing the volumetric
flow, and/or reducing the current passed. Since the current passed is directly
proportional to the total equivalent amount of ions transferred (Section 2.4.2),
the simplest way of achieving additional desalination is by simply directing the
product from the first passage through half the number of cell pairs in the second
passage, thereby doubling the flow rate whilst leaving the current constant. This
is known as hydraulic staging (Fig. 2.22). If further desalination is required, it
may become expedient to reduce the current across the stack. This is referred to
as electrical staging. It is normal to combine hydraulic with electrical staging
to achieve reasonable desalination levels.
First stage Second stage
Figure 2.2 1 Twin-pass ROsystem (permeate staged)