Page 155 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 155
Honda Motor Co. Ltd 137
T DETERIORATION-
2 DETERMINING VALUE
JUDGED AS
QUALlF IED
0 0
JUDGED AS
0 DETERIORATED
'-=-,CRUISING SATURATION
1 TEMPERATURE
. Q
)I0- 300 550 ("c 1
I
DETERIORATED CAT
Fig. 65 (from US5325664)
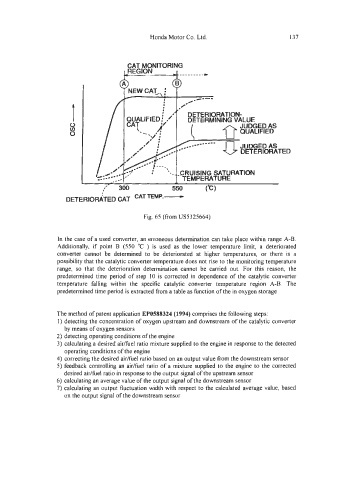
In the case of a used converter, an erroneous determination can take place within range A-B.
Additionally, if point B (550 "C ) is used as the lower temperature limit, a deteriorated
converter cannot be determined to be deteriorated at higher temperatures, or there is a
possibility that the catalytic converter temperature does not rise to the monitoring temperature
range, so that the deterioration determination cannot be carried out. For this reason, the
predetermined time period of step IO is corrected in dependence of the catalytic converter
temperature falling within the specific catalytic converter temperature region A-B. The
predetermined time period is extracted from a table as function of the in oxygen storage
The method of patent application EP0588324 (1994) comprises the following steps:
1) detecting the concentration of oxygen upstream and downstream of the catalytic converter
by means of oxygen sensors
2) detecting operating conditions of the engine
3) calculating a desired air/fbel ratio mixture supplied to the engine in response to the detected
operating conditions of the engine
4) correcting the desired aidfuel ratio based on an output value from the downstream sensor
5) feedback controlling an aidfuel ratio of a mixture supplied to the engine to the corrected
desired aidfie! ratio in response to the output signal of the upstream sensor
6) calculating an average value of the output signal of the downstream sensor
7) calculating an output fluctuation width with respect to the calculated average value, based
on the output signal of the downstream sensor