Page 296 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 296
278 Methods for Monitoring and Diagnosing the Efficiency of Catalytic Converters
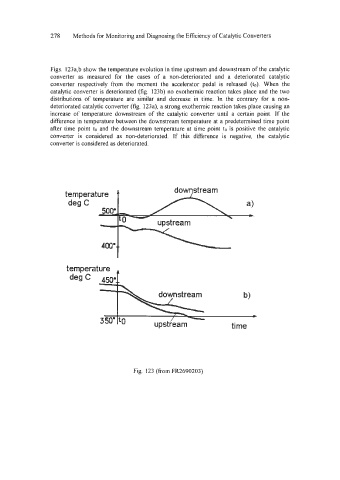
Figs. 123a,b show the temperature evolution in time upstream and downstream of the catalytic
converter as measured for the cases of a non-deteriorated and a deteriorated catalytic
converter respectively from the moment the accelerator pedal is released (to). When the
catalytic converter is deteriorated (fig. 123b) no exothermic reaction takes place and the two
distributions of temperature are similar and decrease in time. In the contrary for a non-
deteriorated catalytic converter (fig. 123a), a strong exothermic reaction takes place causing an
increase of temperature downstream of the catalytic converter until a certain point. If the
difference in temperature between the downstream temperature at a predetermined time point
after time point to and the downstream temperature at time point to is positive the catalytic
converter is considered as non-deteriorated. If this difference is negative, the catalytic
converter is considered as deteriorated.
- -
uey t
501
400'+
I
Fig. 123 (from FR2690203)