Page 299 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 299
Siemens - Bayerische Motoren Werke - Mercedes Benz 28 1
3) measuring the temperature T2 of the heated exhaust gases between the burner and the
catalytic converter at a time point t2
4) comparing the measured temperature T2 with a predetermined threshold To
5) determining that the system is deteriorated when Tz<To.
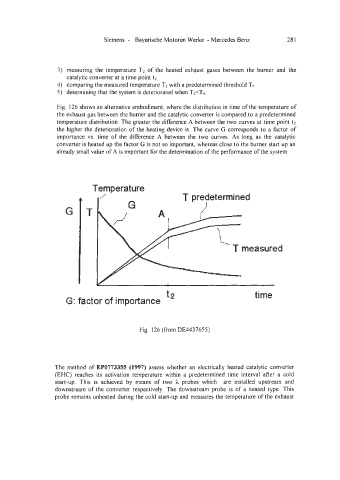
Fig. 126 shows an alternative embodiment, where the distribution in time of the temperature of
the exhaust gas between the burner and the catalytic converter is compared to a Predetermined
temperature distribution. The greater the difference A between the two curves at time point t2
the higher the deterioration of the heating device is. The curve G corresponds to a factor of
importance vs. time of the difference A between the two curves. As long as the catalytic
converter is heated up the factor G is not so important, whereas close to the burner start up an
already small value of A is important for the determination of the performance of the system.
Temperature
G T
f2 time
G: factor of importance
Fig. 126 (from DE4437655)
The method of EP0773355 (1997) assess whether an electrically heated catalytic converter
(EHC) reaches its activation temperature within a predetermined time interval after a cold
start-up. This is achieved by means of two h probes which are installed upstream and
downstream of the converter respectively. The downstream probe is of a heated type. This
probe remains unheated during the cold start-up and measures the temperature of the exhaust