Page 298 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 298
280 Methods for Monitoring and Diagnosing the Eficiency of Catalytic Converters
The method of W09517588 (1995) monitors the condition of a secondary catalytic converter
installed upstream of a main catalytic converter and comprises the following steps:
1) measuring the temperature downstream of the secondary catalytic converter at the
beginning and end of a predetermined idling phase, over a predetermined number of idling
phases, following a power phase under predetermined operating conditions of the engine
2) forming the temperature difference between the temperatures measured at the beginning
and end of each predetermined idling phase
3) forming the sum of the results of temperature differences calculating the total duration of
the idling phases
4) forming an average temperature quotient from the sum of temperature differences and the
total duration of the idling phases
5) comparing the average temperature gradient thus formed with a predetermined threshold
6) assessing the deterioration of the catalytic converter when the average temperature
gradient is higher than the predetermined threshold
-
I- -- ----
. -...
Temaera tiire
t efficient c
I l/\di eteriorated converter
t2 time
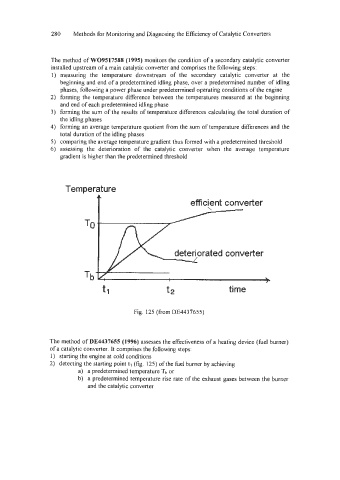
Fig. 125 @om DE4437655)
The method of DE4437655 (1996) assesses the effectiveness of a heating device (fuel burner)
of a catalytic converter. It comprises the following steps:
1) starting the engine at cold conditions
2) detecting the starting point tl (fig. 125) ofthe fuel burner by achieving
a) a predetermined temperature Th or
b) a predetermined temperature rise rate of the exhaust gases between the burner
and the catalytic converter