Page 297 - Methods For Monitoring And Diagnosing The Efficiency Of Catalytic Converters A Patent - oriented Survey
P. 297
Siemens - Bayerische Motoren Werke - Mercedes Benz 279
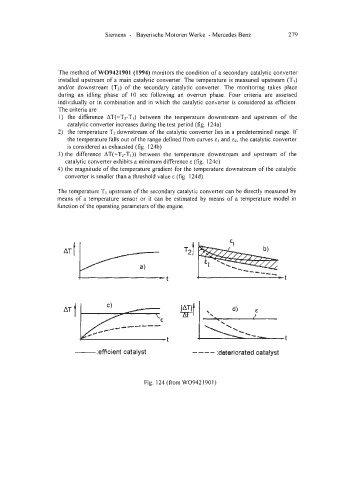
The method of W09421901 (1994) monitors the condition of a secondary catalytic converter
installed upstream of a main catalytic converter. The temperature is measured upstream (TI)
andor downstream (T2) of the secondary catalytic converter. The monitoring takes place
during an idling phase of 10 sec following an overrun phase. Four criteria are assessed
individually or in combination and in which the catalytic converter is considered as efficient.
The criteria are:
1) the difference AT(=Tz-Tl) between the temperature downstream and upstream of the
catalytic converter increases during the test period (fig. 124a)
2) the temperature Tz downstream of the catalytic converter lies in a predetermined range. If
the temperature falls out of the range defined from curves and E~, the catalytic converter
is considered as exhausted (fig. 124b)
3) the difference AT(=T2-TI)) between the temperature downstream and upstream of the
catalytic converter exhibits a minimum difference E (fig. 124c)
4) the magnitude of the temperature gradient for the temperature downstream of the catalytic
converter is smaller than a threshold value E (fig. 124d).
The temperature TI upstream of the secondary catalytic converter can be directly measured by
means of a temperature sensor or it can be estimated by means of a temperature model in
function of the operating parameters of the engine.
T2 t
t
t
:efficient catalyst ---- :deteriorated catalyst
Fig. 124 (from W09421901)