Page 282 - Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
P. 282
252 Modeling of Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design
contacts only fresh catalyst. The recirculation further provides more
complexity to the construction, which gives it a lower rating.
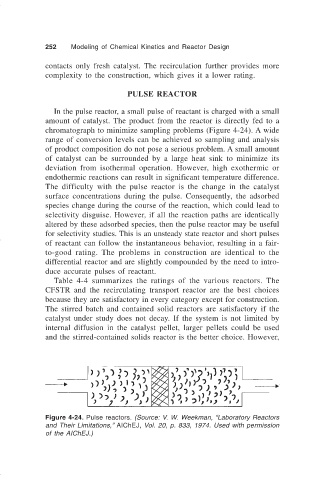
PULSE REACTOR
In the pulse reactor, a small pulse of reactant is charged with a small
amount of catalyst. The product from the reactor is directly fed to a
chromatograph to minimize sampling problems (Figure 4-24). A wide
range of conversion levels can be achieved so sampling and analysis
of product composition do not pose a serious problem. A small amount
of catalyst can be surrounded by a large heat sink to minimize its
deviation from isothermal operation. However, high exothermic or
endothermic reactions can result in significant temperature difference.
The difficulty with the pulse reactor is the change in the catalyst
surface concentrations during the pulse. Consequently, the adsorbed
species change during the course of the reaction, which could lead to
selectivity disguise. However, if all the reaction paths are identically
altered by these adsorbed species, then the pulse reactor may be useful
for selectivity studies. This is an unsteady state reactor and short pulses
of reactant can follow the instantaneous behavior, resulting in a fair-
to-good rating. The problems in construction are identical to the
differential reactor and are slightly compounded by the need to intro-
duce accurate pulses of reactant.
Table 4-4 summarizes the ratings of the various reactors. The
CFSTR and the recirculating transport reactor are the best choices
because they are satisfactory in every category except for construction.
The stirred batch and contained solid reactors are satisfactory if the
catalyst under study does not decay. If the system is not limited by
internal diffusion in the catalyst pellet, larger pellets could be used
and the stirred-contained solids reactor is the better choice. However,
Figure 4-24. Pulse reactors. (Source: V. W. Weekman, “Laboratory Reactors
and Their Limitations,” AIChEJ, Vol. 20, p. 833, 1974. Used with permission
of the AIChEJ.)