Page 294 - Modern Analytical Chemistry
P. 294
1400-CH09 9/9/99 2:12 PM Page 277
Chapter 9 Titrimetric Methods of Analysis 277
18.0
16.0
14.0
12.0
pCd 10.0
8.0
6.0
4.0
2.0
0.0
0.00 10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00
Volume of titrant (mL)
(a)
1.800
1.600
1.400
Potential (V) 1.000
1.200
0.800
0.600
0.400
0.200
0.000
0 20 40 60 80 100
Volume of titrant (mL)
(b)
8.0
Temperature (°C) Equivalence point
6.0
pCl 4.0
2.0
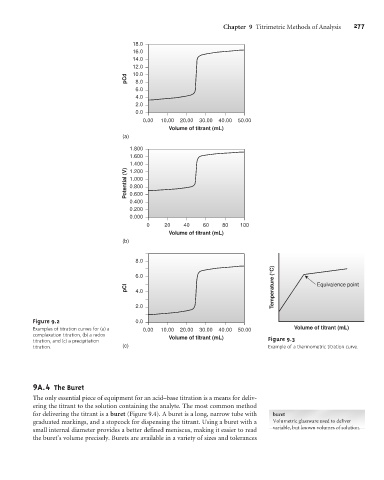
Figure 9.2 0.0
Examples of titration curves for (a) a 0.00 10.00 20.00 30.00 40.00 50.00 Volume of titrant (mL)
complexation titration, (b) a redox Volume of titrant (mL)
titration, and (c) a precipitation Figure 9.3
titration. (c) Example of a thermometric titration curve.
9A.4 The Buret
The only essential piece of equipment for an acid–base titration is a means for deliv-
ering the titrant to the solution containing the analyte. The most common method
for delivering the titrant is a buret (Figure 9.4). A buret is a long, narrow tube with buret
graduated markings, and a stopcock for dispensing the titrant. Using a buret with a Volumetric glassware used to deliver
small internal diameter provides a better defined meniscus, making it easier to read variable, but known volumes of solution.
the buret’s volume precisely. Burets are available in a variety of sizes and tolerances