Page 98 - MODERN ASPECTS OF ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 98
Direct Methanol Fuel Cells
or: 81
Pt( CO) + Pt(OH) ads ↔Pt + Pt( COOH) ads (27)
ads
followed by Eq. (25).
This mechanism takes into account the formation of all the products
detected: CO 2 from steps (23), (25), or (26), formation of formaldehyde
after steps (19) or (19′) and (20) or (20′),and formation of formic acid
after steps (24) or (27).
The infrared spectra exhibit the absorption bands corresponding to
all these species. Adsorbed CO is detected as IR absorption bands around
2050 cm for the linearly bonded species and 1870 cm for the bridge-
-1
-1
bonded species. The presence of CO is clearly indicated by the sharp band
2
at 2345 cm , which appears at higher potentials; the formation of
-1
( CHO) is evidenced by the band at 1690 cm , while that of
-1
ads
( COOH) by weak absorption bands around 1720 cm (see Figs. 6 to
-1
ads
8).
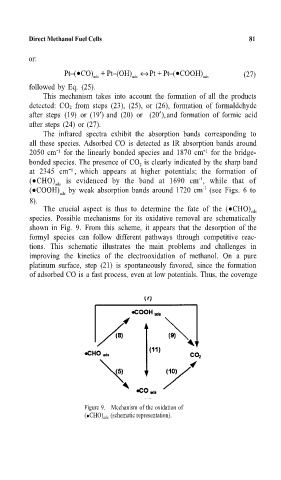
The crucial aspect is thus to determine the fate of the ( CHO) ads
species. Possible mechanisms for its oxidative removal are schematically
shown in Fig. 9. From this scheme, it appears that the desorption of the
formyl species can follow different pathways through competitive reac-
tions. This schematic illustrates the main problems and challenges in
improving the kinetics of the electrooxidation of methanol. On a pure
platinum surface, step (21) is spontaneously favored, since the formation
of adsorbed CO is a fast process, even at low potentials. Thus, the coverage
Figure 9. Mechanism of the oxidation of
( CHO) ads (schematic representation).