Page 142 - Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
P. 142
106 Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
MVDC
BUS
R _ _ R _ _
G ~ ~ _ _ L _ _ L M
~ C C CA1 ~ ~ ~
G1 C1 C5 C13 M1
_ _ R _ _
_ _ L LVAC
CA2 C ~ ~ load
C9 C14 L1
R _ _ R _ _ R
G ~ ~ _ _ L _ _ L _ _ L
~ C C CA3 C
G2 C2 C6 C10
LVDC
load
L2
R _ _ R _ _ R
G ~ ~ _ _ L _ _ L L
~ C C CA4 _ _ C
G3 C3 C7 C11
_ _ R
_ _ L LVDC
load
C
CA5
C12 L3
R _ _ R _ _
G ~ ~ _ _ L _ _ L M
~ C C ~ ~ ~
G4 C4 C8 CA6 C15 M2
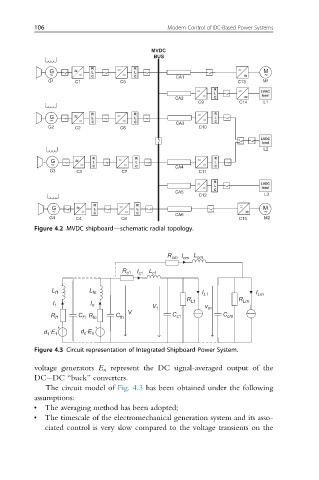
Figure 4.2 MVDC shipboard—schematic radial topology.
R cm I cm L cm
R c1 I L
c1 c1
L f1 L fn I L1 I Lm
R L1 R Lm
I 1 I n V v
V 1 m
C C C C
R f1 f1 R fn fn c1 cm
d ·E 1 d ·E n
1
n
Figure 4.3 Circuit representation of Integrated Shipboard Power System.
voltage generators E n represent the DC signal-averaged output of the
DC DC “buck” converters.
The circuit model of Fig. 4.3 has been obtained under the following
assumptions:
• The averaging method has been adopted;
• The timescale of the electromechanical generation system and its asso-
ciated control is very slow compared to the voltage transients on the