Page 140 - Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
P. 140
104 Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
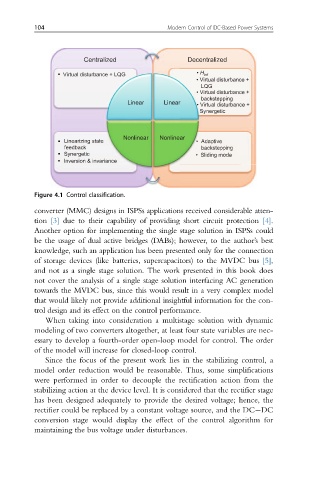
Centralized Decentralized
Virtual disturbance + LQG • H inf
• Virtual disturbance +
LQG
• Virtual disturbance +
backstepping
Linear Linear
• Virtual disturbance +
Synergetic
Nonlinear Nonlinear
Linearizing state • Adaptive
feedback backstepping
Synergetic • Sliding mode
Inversion & invariance
Figure 4.1 Control classification.
converter (MMC) designs in ISPSs applications received considerable atten-
tion [3] due to their capability of providing short circuit protection [4].
Another option for implementing the single stage solution in ISPSs could
be the usage of dual active bridges (DABs); however, to the author’s best
knowledge, such an application has been presented only for the connection
of storage devices (like batteries, supercapacitors) to the MVDC bus [5],
and not as a single stage solution. The work presented in this book does
not cover the analysis of a single stage solution interfacing AC generation
towards the MVDC bus, since this would result in a very complex model
that would likely not provide additional insightful information for the con-
trol design and its effect on the control performance.
When taking into consideration a multistage solution with dynamic
modeling of two converters altogether, at least four state variables are nec-
essary to develop a fourth-order open-loop model for control. The order
of the model will increase for closed-loop control.
Since the focus of the present work lies in the stabilizing control, a
model order reduction would be reasonable. Thus, some simplifications
were performed in order to decouple the rectification action from the
stabilizing action at the device level. It is considered that the rectifier stage
has been designed adequately to provide the desired voltage; hence, the
rectifier could be replaced by a constant voltage source, and the DC DC
conversion stage would display the effect of the control algorithm for
maintaining the bus voltage under disturbances.