Page 256 - Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
P. 256
220 Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
6.1 CASCADED SYSTEM EVALUATION
The cascaded system evaluation is especially useful for decentralized
control approaches, since it is possible to observe directly what the best
potential estimate is, as the estimate directly reflects the load.
The cascaded system consists of one POL converter and one LRC in
which the stabilizing control is evaluated. It offers valuable insight on
how direct changes in the POL control will affect a decentralized control
strategy. The single-generator models are simulated using averaged con-
verters models. The simulations were run with system parameters men-
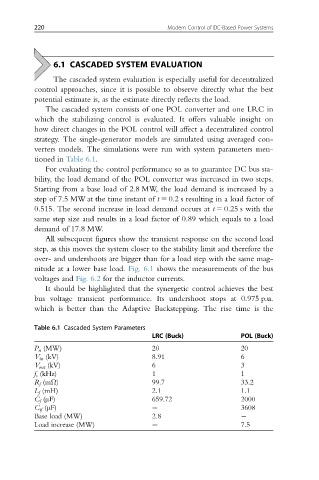
tioned in Table 6.1.
For evaluating the control performance so as to guarantee DC bus sta-
bility, the load demand of the POL converter was increased in two steps.
Starting from a base load of 2.8 MW, the load demand is increased by a
step of 7.5 MW at the time instant of t 5 0.2 s resulting in a load factor of
0.515. The second increase in load demand occurs at t 5 0.25 s with the
same step size and results in a load factor of 0.89 which equals to a load
demand of 17.8 MW.
All subsequent figures show the transient response on the second load
step, as this moves the system closer to the stability limit and therefore the
over- and undershoots are bigger than for a load step with the same mag-
nitude at a lower base load. Fig. 6.1 shows the measurements of the bus
voltages and Fig. 6.2 for the inductor currents.
It should be highlighted that the synergetic control achieves the best
bus voltage transient performance. Its undershoot stops at 0.975 p.u.
which is better than the Adaptive Backstepping. The rise time is the
Table 6.1 Cascaded System Parameters
LRC (Buck) POL (Buck)
P n (MW) 20 20
V in (kV) 8.91 6
V out (kV) 6 3
f s (kHz) 1 1
R f (mΩ) 99.7 33.2
L f (mH) 2.1 1.1
C f (μF) 659.72 2000
C if (μF) 3608
Base load (MW) 2.8
Load increase (MW) 7.5