Page 156 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 156
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 68
determination, where fluorescence is quenched, UV detection is necessary [23].
2.2.3.2—
Phenyl Isothiocyanate (PITC, Edman Reagent)
In 1949, PITC was first introduced by Edman for peptide sequencing [24]. Practically, the chemistry of
this reaction has remained unchanged until now. The derivatives are usually cyclized and rearrange
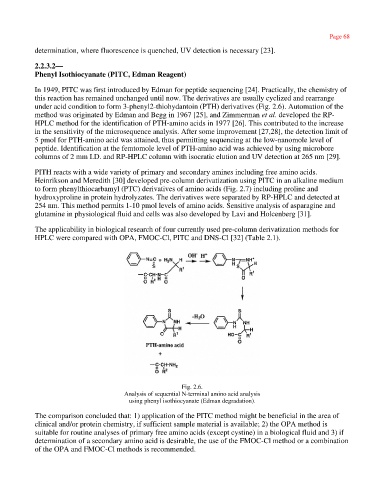
under acid condition to form 3-phenyl2-thiohydantoin (PTH) derivatives (Fig. 2.6). Automation of the
method was originated by Edman and Begg in 1967 [25], and Zimmerman et al. developed the RP-
HPLC method for the identification of PTH-amino acids in 1977 [26]. This contributed to the increase
in the sensitivity of the microsequence analysis. After some improvement [27,28], the detection limit of
5 pmol for PTH-amino acid was attained, thus permitting sequencing at the low-nanomole level of
peptide. Identification at the femtomole level of PTH-amino acid was achieved by using microbore
columns of 2 mm I.D. and RP-HPLC column with isocratic elution and UV detection at 265 nm [29].
PITH reacts with a wide variety of primary and secondary amines including free amino acids.
Heinrikson and Meredith [30] developed pre-column derivatization using PITC in an alkaline medium
to form phenylthiocarbamyl (PTC) derivatives of amino acids (Fig. 2.7) including proline and
hydroxyproline in protein hydrolyzates. The derivatives were separated by RP-HPLC and detected at
254 nm. This method permits 1-10 pmol levels of amino acids. Sensitive analysis of asparagine and
glutamine in physiological fluid and cells was also developed by Lavi and Holcenberg [31].
The applicability in biological research of four currently used pre-column derivatization methods for
HPLC were compared with OPA, FMOC-Cl, PITC and DNS-Cl [32] (Table 2.1).
Fig. 2.6.
Analysis of sequential N-terminal amino acid analysis
using phenyl isothiocyanate (Edman degradation).
The comparison concluded that: 1) application of the PITC method might be beneficial in the area of
clinical and/or protein chemistry, if sufficient sample material is available; 2) the OPA method is
suitable for routine analyses of primary free amino acids (except cystine) in a biological fluid and 3) if
determination of a secondary amino acid is desirable, the use of the FMOC-Cl method or a combination
of the OPA and FMOC-Cl methods is recommended.
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_68.html 30/09/2003