Page 158 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 158
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 69
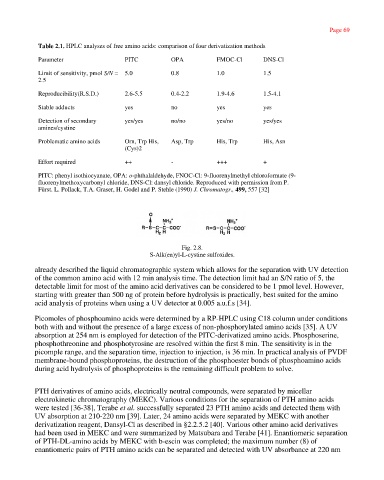
Table 2.1. HPLC analyses of free amino acids: comparison of four derivatization methods
Parameter PITC OPA FMOC-Cl DNS-Cl
Limit of sensitivity, pmol S/N = 5.0 0.8 1.0 1.5
2.5
Reproducibility(R.S.D.) 2.6-5.5 0.4-2.2 1.9-4.6 1.5-4.1
Stable adducts yes no yes yes
Detection of secondary yes/yes no/no yes/no yes/yes
amines/cystine
Problematic amino acids Orn, Trp His, Asp, Trp His, Trp His, Asn
(Cys)2
Effort required ++ - +++ +
PITC: phenyl isothiocyanate, OPA: o-phthalaldehyde, FNOC-Cl: 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (9-
fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl chloride, DNS-Cl: dansyl chloride. Reproduced with permission from P.
Fürst. L. Pollack, T.A. Graser, H. Godel and P. Stehle (1990) J. Chromatogr., 499, 557 [32]
Fig. 2.8.
S-Alk(en)yl-L-cystine sulfoxides.
already described the liquid chromatographic system which allows for the separation with UV detection
of the common amino acid with 12 min analysis time. The detection limit had an S/N ratio of 5, the
detectable limit for most of the amino acid derivatives can be considered to be 1 pmol level. However,
starting with greater than 500 ng of protein before hydrolysis is practically, best suited for the amino
acid analysis of proteins when using a UV detector at 0.005 a.u.f.s [34].
Picomoles of phosphoamino acids were determined by a RP-HPLC using C18 column under conditions
both with and without the presence of a large excess of non-phosphorylated amino acids [35]. A UV
absorption at 254 nm is employed for detection of the PITC-derivatized amino acids. Phosphoserine,
phosphothreonine and phosphotyrosine are resolved within the first 8 min. The sensitivity is in the
picomple range, and the separation time, injection to injection, is 36 min. In practical analysis of PVDF
membrane-bound phosphoproteins, the destruction of the phosphoester bonds of phosphoamino acids
during acid hydrolysis of phosphoproteins is the remaining difficult problem to solve.
PTH derivatives of amino acids, electrically neutral compounds, were separated by micellar
electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC). Various conditions for the separation of PTH amino acids
were tested [36-38], Terabe et al. successfully separated 23 PTH amino acids and detected them with
UV absorption at 210-220 nm [39]. Later, 24 amino acids were separated by MEKC with another
derivatization reagent, Dansyl-Cl as described in §2.2.5.2 [40]. Various other amino acid derivatives
had been used in MEKC and were summarized by Matsubara and Terabe [41]. Enantiomeric separation
of PTH-DL-amino acids by MEKC with b-escin was completed; the maximum number (8) of
enantiomeric pairs of PTH amino acids can be separated and detected with UV absorbance at 220 nm
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_69.html 30/09/2003