Page 238 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 238
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 109
from the inferior vena cava. The animals are then infused rapidly via the left ventricle with three times
their estimated blood volume with a solution containing 0.9% NaCl and 100 µM phloretin [(3'), 4'-4,6-
(tetra)trihydroxyaurone] at pH 7.4 to clear the tissues of blood. Phloretin as well as other aurone
flavonoids can displace thyroid hormones from their binding proteins and block deiodination, therefore,
immediately inhibiting the peripheral metabolism of iodothyronines. The tissues to be utilized, usually
brain and liver, are removed rapidly and generally 1.0 g of tissue is used for analysis. The tissues are
homogenized immediately in 6.0 ml of cold 80% ethanol, 0.02 M NaOH and 100 µM phloretin at pH
11.5. The samples are centrifuged and the supernatant is poured into a small beaker. This procedure is
repeated two more times, and the supernatants are combined. The supernatants are dried in a vacuum
oven at 40°C. The residues are then resuspended in 4 ml of water containing 100 µM phloretin at pH
6.0 in order to separate free amino acids from the iodo compounds. The samples are then centrifuged at
105 000 g for 30 min. The supernatants are discarded and the residues are solubilized in 0.02 M NaOH
and 100 µM phloretin at pH 11.5 and frozen until analysis.
Small (2.0 ml volume) vials are used for the derivatization procedure. A 100 µl volume of 0.5 M
NaHCO at pH 9.5 is added to the vials. This is followed with 25-100 µl of tissue or serum extract being
3
added to the buffer. The amount of sample depended upon the tissue being analyzed, the age of the
animal and prior treatment of the animal. Either 25 or 50 µl (0.5 or 1.0 pmol) of the mixed standards are
added to each vial and finally 100 µl of DNS-CL solution (6.0 mg/ml of acetone) are added to each vial.
Several vials containing only standards (0.5 or 1.0 pmol) as well as a blank with buffer only are
prepared for each run. The samples are vortex-mixed and placed in a refrigerator, and the reaction is
allowed to proceed overnight. The following morning the volume of each vial is brought to 1.0ml with
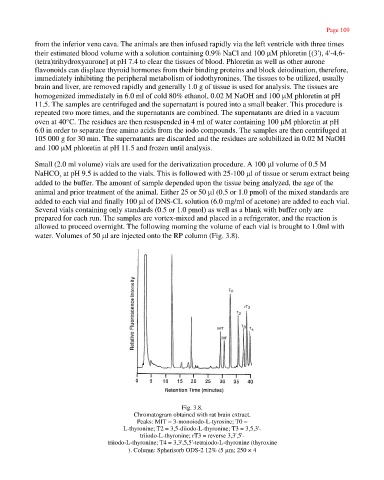
water. Volumes of 50 µl are injected onto the RP column (Fig. 3.8).
Fig. 3.8.
Chromatogram obtained with rat brain extract.
Peaks: MIT = 3-monoiodo-L-tyrosine; T0 =
L-thyronine; T2 = 3,5-diiodo-L-thyronine; T3 = 3,5,3'-
triiodo-L-thyronine; rT3 = reverse 3,3',5'-
triiodo-L-thyronine; T4 = 3,3',5,5'-tetraiodo-L-thyronine (thyroxine
). Column: Spherisorb ODS-2 12% (5 µm; 250 × 4
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_109.ht... 30/09/2003