Page 234 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 234
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 107
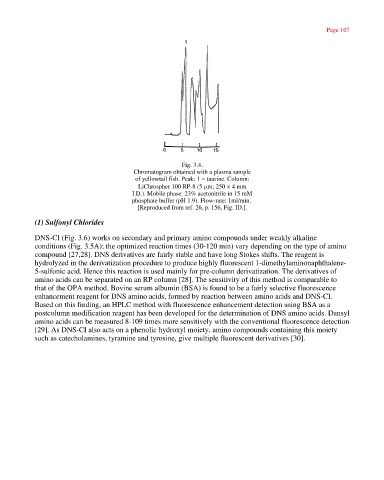
Fig. 3.4.
Chromatogram obtained with a plasma sample
of yellowtail fish. Peak: 1 = taurine. Column:
LiChrospher 100 RP-8 (5 µm; 250 × 4 mm
I.D.). Mobile phase: 23% acetonitrile in 15 mM
phosphate buffer (pH 1.9). Flow-rate: 1ml/min.
[Reproduced from ref. 26, p. 156, Fig. ID.].
(1) Sulfonyl Chlorides
DNS-CI (Fig. 3.6) works on secondary and primary amino compounds under weakly alkaline
conditions (Fig. 3.5A); the optimized reaction times (30-120 min) vary depending on the type of amino
compound [27,28]. DNS derivatives are fairly stable and have long Stokes shifts. The reagent is
hydrolyzed in the derivatization procedure to produce highly fluorescent 1-dimethylaminonaphthalene-
5-sulfonic acid. Hence this reaction is used mainly for pre-column derivatization. The derivatives of
amino acids can be separated on an RP column [28]. The sensitivity of this method is comparable to
that of the OPA method. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is found to be a fairly selective fluorescence
enhancement reagent for DNS amino acids, formed by reaction between amino acids and DNS-CI.
Based on this finding, an HPLC method with fluorescence enhancement detection using BSA as a
postcolumn modification reagent has been developed for the determination of DNS amino acids. Dansyl
amino acids can be measured 8-109 times more sensitively with the conventional fluorescence detection
[29]. As DNS-CI also acts on a phenolic hydroxyl moiety, amino compounds containing this moiety
such as catecholamines, tyramine and tyrosine, give multiple fluorescent derivatives [30].
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_107.ht... 30/09/2003