Page 232 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 232
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 106
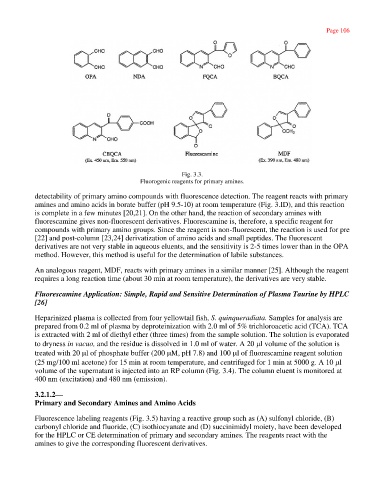
Fig. 3.3.
Fluorogenic reagents for primary amines.
detectability of primary amino compounds with fluorescence detection. The reagent reacts with primary
amines and amino acids in borate buffer (pH 9.5-10) at room temperature (Fig. 3.ID), and this reaction
is complete in a few minutes [20,21]. On the other hand, the reaction of secondary amines with
fluorescamine gives non-fluorescent derivatives. Fluorescamine is, therefore, a specific reagent for
compounds with primary amino groups. Since the reagent is non-fluorescent, the reaction is used for pre
[22] and post-column [23,24] derivatization of amino acids and small peptides. The fluorescent
derivatives are not very stable in aqueous eluents, and the sensitivity is 2-5 times lower than in the OPA
method. However, this method is useful for the determination of labile substances.
An analogous reagent, MDF, reacts with primary amines in a similar manner [25]. Although the reagent
requires a long reaction time (about 30 min at room temperature), the derivatives are very stable.
Fluorescamine Application: Simple, Rapid and Sensitive Determination of Plasma Taurine by HPLC
[26]
Heparinized plasma is collected from four yellowtail fish, S. quinqueradiata. Samples for analysis are
prepared from 0.2 ml of plasma by deproteinization with 2.0 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid (TCA). TCA
is extracted with 2 ml of diethyl ether (three times) from the sample solution. The solution is evaporated
to dryness in vacuo, and the residue is dissolved in 1.0 ml of water. A 20 µl volume of the solution is
treated with 20 µl of phosphate buffer (200 µM, pH 7.8) and 100 µl of fluorescamine reagent solution
(25 mg/100 ml acetone) for 15 min at room temperature, and centrifuged for 1 min at 5000 g. A 10 µl
volume of the supernatant is injected into an RP column (Fig. 3.4). The column eluent is monitored at
400 nm (excitation) and 480 nm (emission).
3.2.1.2—
Primary and Secondary Amines and Amino Acids
Fluorescence labeling reagents (Fig. 3.5) having a reactive group such as (A) sulfonyl chloride, (B)
carbonyl chloride and fluoride, (C) isothiocyanate and (D) succinimidyl moiety, have been developed
for the HPLC or CE determination of primary and secondary amines. The reagents react with the
amines to give the corresponding fluorescent derivatives.
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_106.ht... 30/09/2003