Page 197 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 197
ION–SOLVENT INTERACTIONS 135
one finds
Furthermore, for three degrees of free rotations is calculated with the same
general approach to be 43.85 Adding these components together, one
obtains a calculated entropy for the structure-broken part of model C, that is,
Thus, the total entropy for model C is
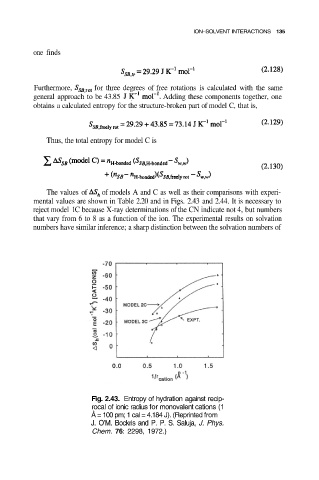
The values of of models A and C as well as their comparisons with experi-
mental values are shown in Table 2.20 and in Figs. 2.43 and 2.44. It is necessary to
reject model 1C because X-ray determinations of the CN indicate not 4, but numbers
that vary from 6 to 8 as a function of the ion. The experimental results on solvation
numbers have similar inference; a sharp distinction between the solvation numbers of
Fig. 2.43. Entropy of hydration against recip-
rocal of ionic radius for monovalent cations (1
Å = 100 pm; 1 cal = 4.184 J). (Reprinted from
J. O’M. Bockris and P. P. S. Saluja, J. Phys.
Chem. 76: 2298, 1972.)