Page 200 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 200
ION–SOLVENT INTERACTIONS 137
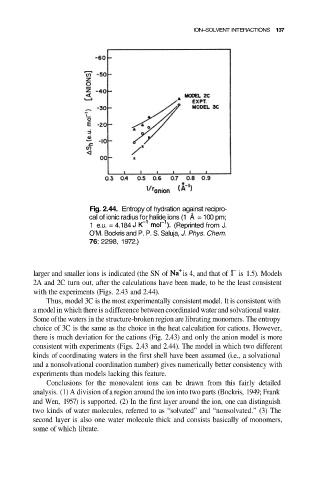
Fig. 2.44. Entropy of hydration against recipro-
cal of ionic radius for halide ions (1 Å = 100 pm;
1 e.u. = 4.184 (Reprinted from J.
O’M. Bockris and P. P. S. Saluja, J. Phys. Chem.
76: 2298, 1972.)
larger and smaller ions is indicated (the SN of is 4, and that of is 1.5). Models
2A and 2C turn out, after the calculations have been made, to be the least consistent
with the experiments (Figs. 2.43 and 2.44).
Thus, model 3C is the most experimentally consistent model. It is consistent with
a model in which there is a difference between coordinated water and solvational water.
Some of the waters in the structure-broken region are librating monomers. The entropy
choice of 3C is the same as the choice in the heat calculation for cations. However,
there is much deviation for the cations (Fig. 2.43) and only the anion model is more
consistent with experiments (Figs. 2.43 and 2.44). The model in which two different
kinds of coordinating waters in the first shell have been assumed (i.e., a solvational
and a nonsolvational coordination number) gives numerically better consistency with
experiments than models lacking this feature.
Conclusions for the monovalent ions can be drawn from this fairly detailed
analysis. (1) A division of a region around the ion into two parts (Bockris, 1949; Frank
and Wen, 1957) is supported. (2) In the first layer around the ion, one can distinguish
two kinds of water molecules, referred to as “solvated” and “nonsolvated.” (3) The
second layer is also one water molecule thick and consists basically of monomers,
some of which librate.