Page 221 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 221
ION–SOLVENT INTERACTIONS 157
An example of an Li-O radial distribution function (calculated by MD) is shown
in Fig. 2.56. From such calculations one can obtain relaxation features of the rotational
and translational motion of the neighboring waters and find the effect of or , for
example.
What is practical in the later 1990s depends upon whether software able to carry
out the computation needed has already been written and is available for about
$ 10,000. It is usually economically impractical for university groups to have a program
written for each calculation, so that one finds oneself sometimes carrying out a
calculation for which there is the software rather than obtaining the software to carry
out the needed calculation.
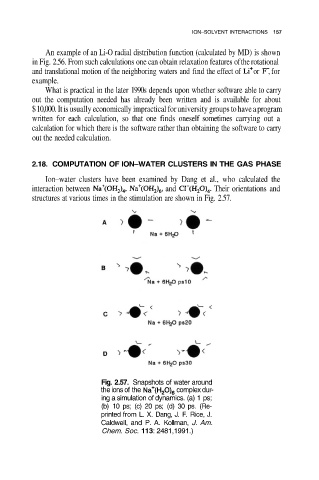
2.18. COMPUTATION OF ION–WATER CLUSTERS IN THE GAS PHASE
Ion–water clusters have been examined by Dang et al., who calculated the
interaction between and Their orientations and
structures at various times in the stimulation are shown in Fig. 2.57.
Fig. 2.57. Snapshots of water around
the ions of the complex dur-
ing a simulation of dynamics. (a) 1 ps;
(b) 10 ps; (c) 20 ps; (d) 30 ps. (Re-
printed from L. X. Dang, J. F. Rice, J.
Caldwell, and P. A. Kollman, J. Am.
Chem. Soc. 113: 2481,1991.)