Page 220 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 220
156 CHAPTER 2
the polarization energy is
and a three-body repulsion term is
where is the induced dipole moment and is the electrostatic field from the
charges. The term is the vector from atom j to atom i, and is the charge on atom
j. The distances and are ion–oxygen distances for the trimer, and is the
oxygen–oxygen distance for the two water molecules in the trimer. Finally, A, C, and
are empirical constants.
An iterative approach is often taken to solve the equations. Iteration may be
continued until the difference in the induced dipole for successive calculations is 0 to
0.1 D. Typically one uses a system of, say, 215 waters for one ion in a cubic cell with
an 1860-pm side. The time step is 1 fs. Coulombic interactions may be cut off at as
little as 800 pm. Each set of calculations involves computer software (the cost of which
may be very high) and various mathematical procedures to solve the equations of
motion.
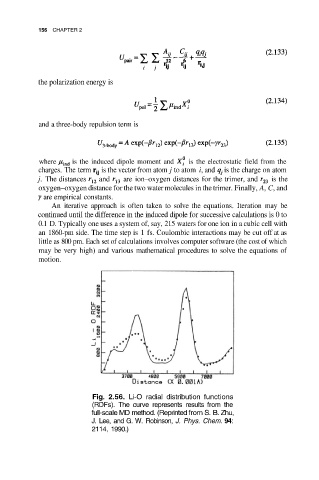
Fig. 2.56. Li-O radial distribution functions
(RDFs). The curve represents results from the
full-scale MD method. (Reprinted from S. B. Zhu,
J. Lee, and G. W. Robinson, J. Phys. Chem. 94:
2114, 1990.)